Due Diligence: Everything Investors Need to Know
Let’s explore what Due Diligence is with GMAJOR. The due diligence process is a comprehensive and detailed investigation conducted to assess various aspects of a business before making an investment or acquisition. In this guide, we’ll cover its definition, types, steps, and benefits to help investors make well-informed and effective decisions.

1. What is Due Diligence?
Due Diligence is a thorough and detailed evaluation process, typically conducted by investors or companies before engaging in transactions such as acquisitions or investments. It involves reviewing, analyzing, and assessing financial, legal, commercial, and sometimes technical information of the target company.
The primary purpose of Due Diligence is to identify potential risks, opportunities, and the true value of the business prior to making investment decisions, ensuring transparency and informed choices. This process helps investors avoid unpleasant surprises after committing financial resources and increases the likelihood of a successful deal.
2. Why Conduct Due Diligence?
Implementing Due Diligence brings essential benefits, especially in investment and M&A transactions:
- Risk Mitigation: Helps investors fully understand the financial, legal, and commercial status of the target business, uncovering potential issues such as bad debts, legal disputes, or operational weaknesses.
- Accurate Valuation: Assesses the real value of the target company by evaluating its assets and profitability, enabling fair price negotiations.
- Transparency: Provides investors with a clear view of strengths and weaknesses, leading to more informed decisions.
- Post-M&A Planning: Supplies necessary insights for integration, resource optimization, and issue resolution after the deal.
- Stakeholder Protection: Ensures that shareholders, investors, and regulators are protected by maintaining transparency and fairness.
In today’s complex business environment, Due Diligence is not optional-it is a critical step for sustainable and successful transactions.

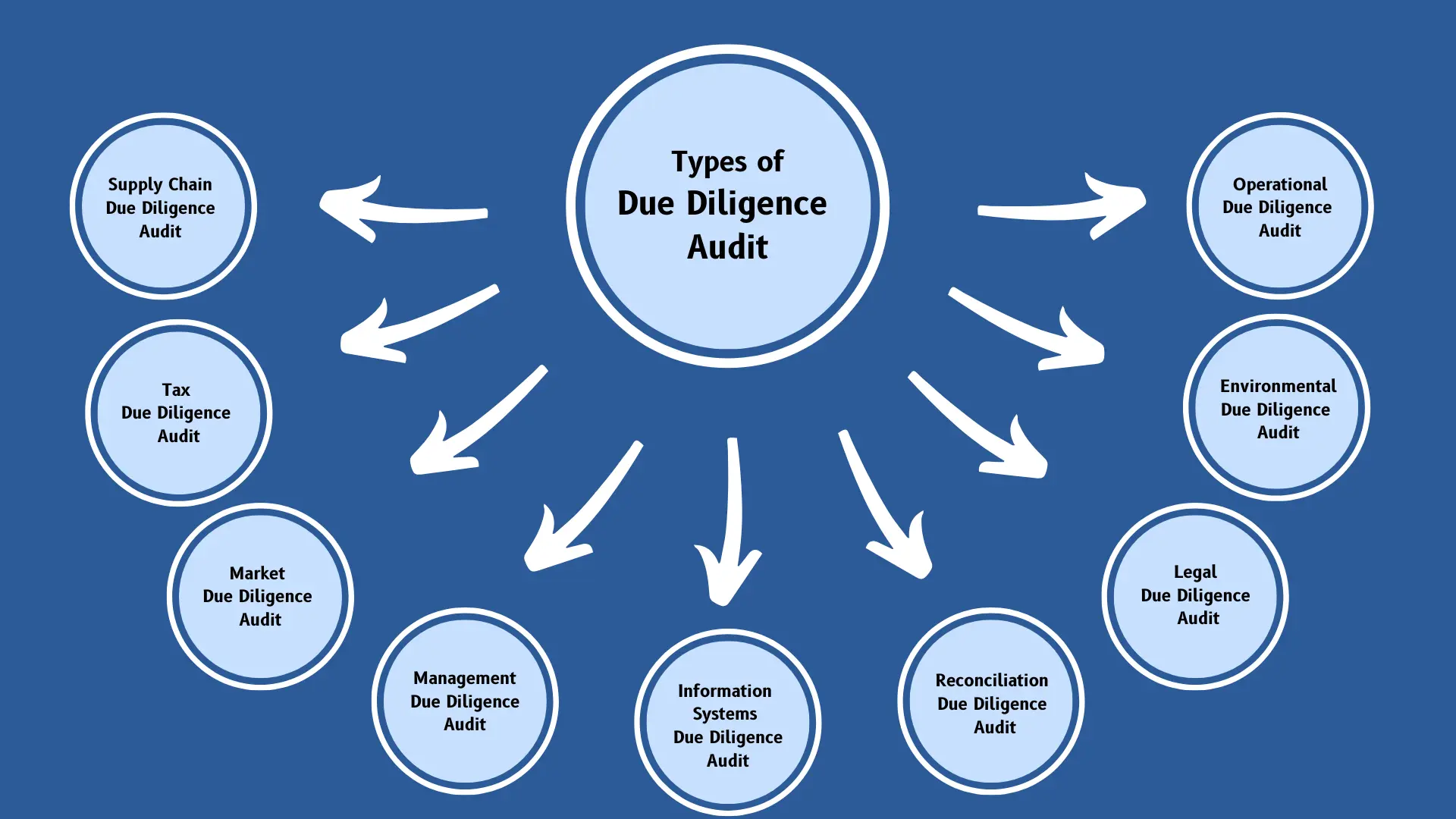
3. Types of Due Diligence
Due Diligence can take various forms, each focusing on a specific aspect of the target company. Below are the most common types of due diligence conducted in business and investment transactions.
3.1. Financial Due Diligence
Financial Due Diligence is a crucial step in evaluating a company before any merger, acquisition, or investment takes place. The main objective is to verify and understand the financial information provided by the target company, including financial statements, cash flows, debts, and other financial commitments.
Conducting Financial Due Diligence helps investors and businesses minimize financial risks by offering a clear and comprehensive view of the company’s financial health. This process plays an essential role in making informed investment decisions and equips buyers with the necessary insights to negotiate optimal deal terms and pricing.
3.2. Commercial Due Diligence
Commercial Due Diligence involves an in-depth analysis of the market environment and the target company’s business strategy. It examines factors such as market positioning, competition, customer base, product portfolio, and industry trends. The main goal is to identify growth potential, market risks, and business development opportunities.
Through Commercial Due Diligence, investors gain a better understanding of the target market and can assess whether the company’s strategy aligns with current market conditions. This enables more accurate investment decisions and enhances the likelihood of transaction success.
3.3. Administrative Due Diligence
Administrative Due Diligence focuses on evaluating the management and administrative operations of the target company. This includes examining the company’s organizational structure, management practices, and the efficiency of operational systems such as IT, HR, and internal management processes.
The purpose of this assessment is to evaluate the company’s ability to manage its resources, handle daily operations effectively, and maintain sound governance. It helps investors understand how well the business is managed and its capacity for sustainable and efficient operations.
3.4. Legal Due Diligence
Legal Due Diligence is a critical component of any transaction, particularly in mergers, acquisitions, or investments. It involves a thorough review and assessment of all legal matters concerning the target company.
By conducting Legal Due Diligence, investors can identify potential legal risks, accurately assess the company’s legal standing, and protect themselves from future liabilities. This ensures that transactions are transparent, compliant, and fair - forming a solid foundation for any investment decision.
3.5. Human Resources Due Diligence
Human Resources (HR) Due Diligence is an important part of assessing a company, especially during mergers or acquisitions. It involves reviewing all HR-related aspects, including workforce structure, management practices, corporate culture, and potential personnel issues that may impact post-transaction operations.
HR Due Diligence not only identifies potential risks but also provides valuable insights for post-merger integration and workforce planning, ensuring that the organization continues to operate efficiently and sustainably after the transaction.
3.6. Asset Due Diligence
Asset Due Diligence is the process of reviewing and verifying a target company’s assets before finalizing any deal. The objective is to confirm the value, condition, and legal status of the assets, ensuring they are free from any hidden legal or physical issues.
This process allows investors to understand the true value of the assets and uncover potential risks that may affect the transaction. Conducting Asset Due Diligence is an essential step to ensure a smooth, transparent, and fair deal.
3.7. Environmental Due Diligence
Environmental Due Diligence evaluates environmental risks and liabilities associated with a company or asset under consideration. The goal is to identify, assess, and manage environmental issues that could affect the transaction’s value or result in future legal responsibilities.
Performing Environmental Due Diligence helps investors avoid financial risks related to environmental compliance and ensures the company operates sustainably and responsibly - aligning with modern corporate social responsibility (CSR) standards.
3.8. Tax Due Diligence
Tax Due Diligence involves examining all tax-related matters of the target company before completing a transaction. The purpose is to ensure full compliance with tax regulations and identify any potential tax liabilities that could affect the deal.
This assessment enables investors to understand the company’s tax position, evaluate related risks, and plan financial strategies more effectively. Tax Due Diligence is a key step in ensuring fair and compliant transactions.
3.9. Intellectual Property Due Diligence
Intellectual Property (IP) Due Diligence is the process of reviewing, evaluating, and verifying the target company’s intellectual property assets in the context of an acquisition, merger, or investment. The main goal is to determine the value, scope of protection, and any potential legal risks related to IP ownership.
Conducting IP Due Diligence helps investors understand the strategic and financial importance of the company’s IP assets while identifying growth opportunities and mitigating potential risks - ensuring that the transaction is transparent and well-grounded.
3.10. Technical Due Diligence
Technical Due Diligence is a detailed evaluation of the technical aspects of a company or project prior to investment or acquisition. It covers infrastructure quality, technology systems, and operational processes. The goal is to ensure that the company’s assets and systems meet current standards and are capable of supporting future business operations.
This includes assessing IT systems, equipment reliability, and identifying any underlying technical issues that could impact business performance or valuation. Conducting Technical Due Diligence allows investors to make well-informed decisions based on accurate technical insights and minimize unforeseen risks.
4. Due Diligence Process
The Due Diligence process within a company typically follows several key stages designed to provide a comprehensive assessment of the target firm’s legal, financial, and technical standing. This process plays a crucial role in investment and acquisition decisions, ensuring that investors have a complete understanding of the company’s current status and growth potential.
4.1. Collecting Data on the Company’s Total Valuation (Market Capitalization)
To determine a company’s market capitalization, it is essential to identify the total number of outstanding shares and the current market price per share. The number of outstanding shares can be found in the company’s financial reports or on the stock exchange website. The share price, which fluctuates continuously, can be accessed through online market data platforms. Multiplying these two figures yields the company’s total market capitalization - representing its overall market value.
4.2. Updating Revenue, Profit, and Deposit Trends
Tracking the trends in revenue, profit, and deposits is a fundamental part of evaluating a company’s financial performance:
- Collect financial statements: Review quarterly and annual financial reports to identify revenue and profit patterns over time.
- Analyze deposits: Examine deposits, guarantees, and collateral to assess the company’s financial capacity and obligations.
- Identify trends and compare: Compare data with previous periods and industry benchmarks to evaluate performance and stability.
This analysis helps investors understand the company’s operational efficiency and future growth potential.
4.3. Conducting Industry and Competitor Analysis
Analyzing the target company’s competitive landscape and industry context provides insight into its market position:
- Gather competitor information: Study key competitors, including their financials, product portfolios, market share, and strategies.
- Assess the industry: Evaluate industry trends, technological innovation, and external factors such as regulations and macroeconomic conditions.
- Benchmark performance: Compare the target company’s results with competitors and industry averages to identify strengths, weaknesses, and growth opportunities.
This step enables investors to recognize both risks and opportunities, forming a strategic foundation for investment decisions.

4.4. Evaluating and Assigning Management Authority
This stage focuses on assessing the leadership team’s competence and structuring management for post-transaction efficiency:
- Management evaluation: Review the skills, experience, and track record of the leadership team, as well as their alignment with the company’s long-term goals.
- Authority structuring: Define management hierarchies and determine the optimal structure for post-acquisition operations. Recommend necessary adjustments to improve efficiency.
Through this, investors can assess the company’s leadership capability and its ability to execute strategies effectively.
4.5. Preparing the Balance Sheet
Creating a balance sheet provides a clear view of the target company’s financial position:
- Collect financial data: Gather information from financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports.
- Reconstruct the balance sheet: Reflect accurate asset, liability, and equity positions.
- Analyze and evaluate: Use the balance sheet to assess liquidity, debt levels, and overall financial stability.
This step enables investors to evaluate financial strength and make informed investment decisions.
4.6. Analyzing Stock Performance History
Assessing the company’s stock performance over time provides insights into its financial stability and market perception:
- Gather historical data: Review past stock prices, including opening, closing, high, and low prices, along with trading volume.
- Analyze price trends: Identify long-term and short-term stock price movements and market reactions to company-specific events.
- Evaluate risk and performance: Use historical patterns to assess volatility, risk levels, and return potential.
This analysis helps investors understand how the market values the company and anticipate potential investment risks.
4.7. Assessing Potential Stock Dilution
Evaluating the likelihood of stock dilution helps investors understand how future share issuances may affect their ownership and investment value:
- Review issuance plans: Examine any existing or planned stock issuances, such as stock options, employee share programs, or new offerings.
- Assess impact: Analyze how new issuances might affect shareholder ownership percentages and stock value.
- Consider financial strategy: Evaluate the strategic purpose behind new stock issuances, such as raising capital for expansion or debt repayment.
This step ensures investors can gauge how dilution may influence their returns and overall equity value.
4.8. Conducting the Due Diligence Meeting
The Due Diligence Meeting is a key phase for information exchange, clarification, and decision-making:
- Preparation: Plan the meeting by identifying participants, agenda topics, and required documentation. Ensure all parties are well-informed beforehand.
- Execution: Lead discussions based on the agenda, addressing major topics such as financial, legal, and technical findings. Analyze collected data collaboratively.
- Conclusion: Summarize findings, outline next steps, and assign follow-up actions based on the insights discussed.
This meeting allows all parties to evaluate risks and opportunities directly, align expectations, and strengthen mutual understanding - paving the way for informed and transparent decision-making.
5. What is a Due Diligence Meeting?
A Due Diligence Meeting is a key step before finalizing a transaction or investment. It involves investors, buyers, sellers, and advisors (lawyers, accountants, financial experts). The purpose is to review findings, address risks and opportunities, resolve outstanding issues, and determine next steps. It ensures clarity and alignment among all parties before closing the deal.

6. Challenges and Considerations
Challenges:
- Data Collection: Gathering complete and accurate information from the seller can be difficult, especially when data is limited, outdated, or inconsistently documented.
- Time and Cost: Due Diligence can be both time-consuming and costly, particularly in large-scale or complex transactions that require extensive verification.
- Specialized Expertise: The process demands a highly skilled team capable of analyzing financial, legal, and technical data - which can be challenging if the right experts are not available.
- Hidden Risks: Certain issues may remain undiscovered during the Due Diligence phase, potentially leading to unexpected complications after the transaction closes.
Considerations:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish clear Due Diligence goals to ensure the collected information is relevant, comprehensive, and aligned with investment needs.
- Engage Experts: Involve professionals from various fields - including legal, financial, environmental, and market analysis - to obtain a holistic evaluation.
- Conduct Multi-Dimensional Analysis: Go beyond current figures by examining historical trends and benchmarking against industry standards.
- Ensure Confidentiality: Protect sensitive data and strictly adhere to confidentiality and compliance requirements throughout the process.
- Prepare for Contingencies: Develop backup strategies for potential risks identified during the Due Diligence review to mitigate post-transaction uncertainties.
7. Difference Between Due Diligence and Audit
Due Diligence and Audit are both important processes in the business and financial world; however, they differ in purpose, scope, and approach.
7.1. Due Diligence
- Purpose: Due Diligence is the process of investigating and evaluating a business or asset before proceeding with a transaction such as a merger, acquisition, or investment. Its main goal is to identify, understand, and assess risks, value, and potential opportunities associated with the deal.
Scope: It covers multiple aspects, including legal, financial, technical, environmental, and market factors. The process not only examines financial statements but also evaluates management practices, operational capacity, and legal compliance. - Proactiveness: Usually, the buyer or investor takes the initiative to conduct Due Diligence to ensure they have sufficient and accurate information before making an investment decision.
7.2. Audit
- Purpose: An audit aims to verify and assess the accuracy, fairness, and reliability of a company’s financial statements. Its primary goal is to ensure that these statements accurately reflect the company’s financial position and performance.
- Scope: Focuses mainly on financial statements, accounting records, and related transactions, conducted according to established accounting and auditing standards.
- Independence: Typically performed by an independent third party, such as a professional auditing firm, to ensure objectivity and prevent conflicts of interest.

Overall Comparison
While Due Diligence provides a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of a business prior to investment or acquisition, Audit focuses primarily on verifying the accuracy of reported financial information. In essence, financial audit can be considered a component of the Due Diligence process, but Due Diligence goes further by evaluating broader aspects of the business, including legal, operational, and market dimensions.
Conclusion
Due Diligence is a cornerstone of modern investment and M&A activities. It provides investors with a 360-degree view of the target company, uncovering risks, validating opportunities, and ensuring transparency. Unlike audits, which primarily confirm financial accuracy, Due Diligence evaluates the broader landscape-covering legal, commercial, environmental, and operational aspects.
In an increasingly complex and competitive global market, conducting thorough Due Diligence not only safeguards investors from hidden risks but also lays the foundation for sustainable growth, successful integration, and long-term value creation.